Foreign rental income is an enticing avenue for investment, offering the potential for steady returns in the global real estate market. However, investors must understand the tax implications when earning income from properties outside the United States.
Here at Universal Tax Professionals, we provide personalized US expat tax services tailored to the unique needs of Americans living abroad. We understand the intricacies and nuances of US expat taxation including having to deal with reporting your foreign rental income.
Key Summary of IRS Foreign Rental Income
-
Foreign rental income must be reported on your US tax return using Form 1040 and Schedule E.
-
Currency fluctuations, local property laws, and proper record-keeping all play major roles in correctly tracking and reporting foreign rental income.
-
Depreciation of foreign rental property, calculated under the 30-year ADS method, reduces taxable income and plays a key role in optimizing US tax liability.
-
Tools like the Foreign Tax Credit (FTC) and applicable tax treaties help prevent double taxation on foreign rental income.
-
Taxpayers may also benefit from the Qualified Business Income Deduction (QBID) when foreign rental activity qualifies as a trade or business.
Basics of Foreign Rental Income
Foreign rental income is a revenue source arising from leasing out property outside the United States. It is a compelling investment opportunity that can yield substantial returns, but it also comes with its own set of unique considerations, particularly in taxation. Here are some aspects you must comprehend when dealing with foreign rental income.
Diverse Property Types
Foreign rental properties can take various forms – from vacation homes, apartments, and condominiums to commercial spaces and agricultural land. Each type has its own nuances regarding rental agreements, maintenance, and potential income streams.
Currency Exchange and Exchange Rates
Dealing with foreign rental income introduces the need to navigate currency exchange rates. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the actual income received, and understanding how to account for these changes is important for accurate financial and tax planning.
Local Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Countries have distinct legal and regulatory systems governing property ownership and rental agreements. Familiarizing yourself with the specific laws and requirements of the country where your property is located is essential to ensure compliance and avoid legal complications.
IRS Filing Obligations and Reporting Requirements
Understanding your filing obligations and reporting requirements in the United States for foreign rental income is imperative. The IRS leaves no room for ambiguity – all income must be accurately reported.
Foreign rental income is not exempt from U.S. taxation. No matter where your property is located, the IRS requires you to report this income on your U.S. tax return. This rule applies to all foreign rental properties—whether you are a US expat living in the UK earning income from a cottage in the English countryside, or a US expat living in Japan renting out an apartment in the heart of Tokyo.
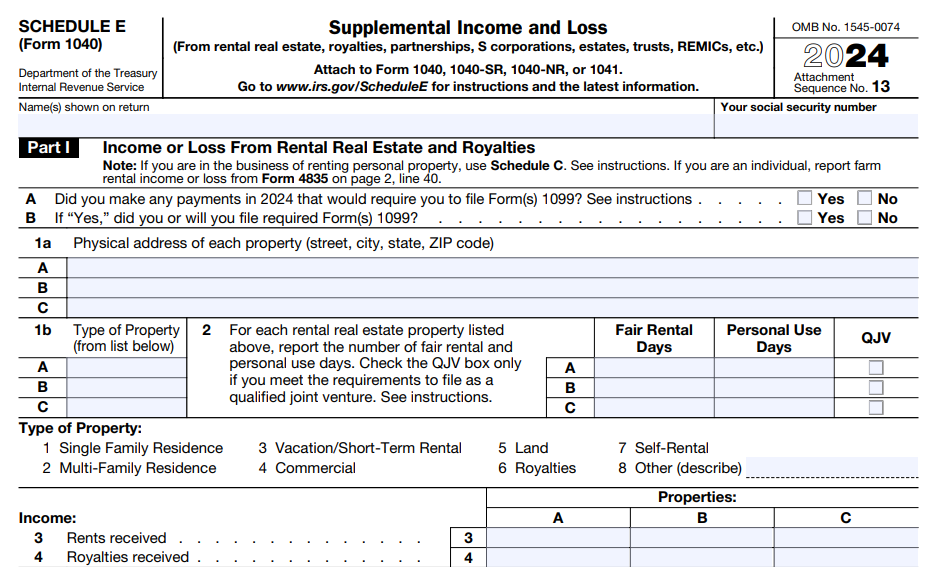
Form 1040 and Schedule E
The cornerstone of reporting foreign rental income lies in Form 1040, specifically Schedule E – Supplemental Income and Loss. This form is designed for the reporting of rental income and expenses. It’s vital to provide accurate and detailed information about each foreign property you own, including the type of property, its location, and the income it generates.
Meticulous Record-Keeping of Income and Expenses
Maintaining thorough records is indispensable to reporting foreign rental income accurately. These records must include documentation of rental agreements, income receipts, and all expenses related to the property. Such meticulous record-keeping is a critical safeguard against potential discrepancies or audits.
Joint Ownership and Reporting Responsibilities
In cases where a foreign rental property is jointly owned, clear communication about reporting responsibilities is essential. Each co-owner must know their obligation to report their share of the income. Hence, proper coordination is key to ensuring income is accurately apportioned and declared.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to report foreign rental income can lead to severe repercussions. Non-compliance penalties can include substantial fines, interest on unpaid taxes, and even legal action. The IRS has sophisticated systems to detect inconsistencies, so accuracy and honesty are paramount.
Integration with Foreign Reporting Requirements
It is also important to understand that reporting foreign rental income to the IRS may necessitate compliance with the tax laws of the country where the property is located. This could involve filing returns or declarations with the foreign tax authority. Therefore, ensuring alignment with both US and foreign tax regulations is crucial.
Foreign Tax Credit and Avoidance of Double Taxation
The Foreign Tax Credit (FTC) helps prevent double taxation by letting US taxpayers offset their US tax liability with taxes paid to a foreign country on foreign rental income. This ensures the same income isn’t taxed twice.
To claim the FTC, property owners must keep clear documentation of foreign tax payments—especially if they own multiple foreign rental properties. If the credit exceeds US tax owed, it can be carried back one year or carried forward to future years. However, the FTC is limited to the amount of US tax attributed to foreign-sourced income and cannot reduce tax on unrelated income.
Depreciation of Foreign Rental Property
Depreciation is an important tax benefit for owners of foreign rental property, allowing you to recover the cost of the building over time. Unlike U.S. property, foreign residential rental property must be depreciated using the Alternative Depreciation System (ADS) with a 30-year recovery period.
This spreads deductions over a longer timeframe but still reduces taxable foreign rental income each year. To claim depreciation, you must track the property’s cost basis, improvements, and land value (which is not depreciable). Proper depreciation is essential for accurate reporting, long-term tax planning, and minimizing overall US tax liability on foreign rental income.
Tax Treaty Benefits
Tax treaties, or bilateral tax agreements, are instruments to prevent double taxation on foreign rental income. These agreements are negotiated between countries to regulate the tax treatment of income earned by residents of one country in the other country.
For property owners, a tax treaty can provide substantial relief and benefits. Typically, tax treaties include provisions that allocate taxing rights between the two countries involved. These provisions may specify which country has the primary right to tax certain types of income, including foreign rental income.
Moreover, tax treaties often outline mechanisms for obtaining relief from double taxation. Such relief can be granted through various means, including tax credits, exemptions, or deductions. Understanding the specifics of the tax treaty between the US and the country where your rental property is located is essential for optimizing your tax position.
Qualified Business Income Deduction (QBID)
Another factor that needs to be considered in optimizing tax returns and ensuring compliance with tax regulations is maximizing available deductions. One significant deduction that can greatly impact the taxable income derived from foreign rental income is the Qualified Business Income Deduction (QBID).
Understanding QBID and Its Relevance to Foreign Rental Income
The QBID allows eligible taxpayers to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income from their taxable income. This provision was designed to stimulate economic growth by providing tax relief to small businesses and pass-through entities, including those involved in foreign real estate held through partnerships, LLCs, S corporations, and sole proprietorships.
For owners of foreign rental properties, QBID can be a powerful tool. When foreign rental income comes from a pass-through entity, a portion of that income may be excluded from taxable income, improving overall tax efficiency and supporting accurate foreign real estate tax reporting.
Qualifying for QBID and Limitations
Eligibility for QBID is contingent on several factors, including the type of business and the individual’s total taxable income. For property owners, certain rental activities may qualify for the QBID, provided they meet specific criteria. For example, the property must be operated as a trade or business, and the owner must materially participate in the rental management.
It is critical to note that limitations apply, and the calculation of the QBID can be intricate. For high-income individuals or those involved in specified service businesses, such as law, health, and financial services, additional rules may come into play. Seeking guidance from a tax professional well-versed in international real estate taxation is recommended to ensure accurate compliance with QBID regulations.
Maximizing QBID Benefits for Foreign Rental Income
For property owners with foreign rental holdings, leveraging the QBID involves meticulous planning and understanding of the intricate tax rules. This may entail structuring the ownership of the property through a pass-through entity or ensuring that the rental activity meets the necessary criteria to qualify for the deduction.
Thorough documentation of rental income, expenses, and operational activities is crucial. Strong record-keeping not only supports accurate foreign real estate tax reporting but also strengthens the taxpayer’s ability to substantiate QBID claims and fully benefit from the deduction.
Key Takeaways for Having Foreign Rental Income
Managing foreign rental income demands careful attention to US tax regulations and international considerations. Ensure you accurately report all foreign rental income on your US tax return using Form 1040 and Schedule E.
Be aware of the concept of permanent establishment and consider any applicable tax treaties to avoid double taxation. Leverage tools like the Foreign Tax Credit and the Qualified Business Income Deduction (QBID) to optimize your tax position.
Keep meticulous records, consider currency exchange rates, and seek professional guidance from a tax advisor well-versed in international taxation to successfully navigate this complex financial landscape. Compliance, transparency, and strategic planning are key to maximizing returns on your foreign rental investments while remaining within the bounds of the law.